Refraction through Spherical Surface and Lens
Refraction through Spherical Surface and Lens: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Optical Centre of Lens, Radii of Curvatures of a Lens,Focal Length of a Lens and Centres of Curvature of a Lens etc.
Important Questions on Refraction through Spherical Surface and Lens
An object is placed in front of a thin convex lens of focal length 30 cm and a plane mirror is placed 15 cm behind the lens. If the final image of the object coincides with the object, the distance of the object from the lens is
A thin lens of focal length and its aperture has a diameter . It forms an image of intensity . Now the central part of the aperture upto diameter is blocked by an opaque paper. The focal length and image intensity would change to
Parallel beam of light is incident on a system of two convex lenses of focal lengths and . What should be the distance between the two lenses so that rays after refraction from both the lenses pass undeviated
A plano-convex lens has maximum thickness of 1 mm. If diameter of its aperture is 4 cm, then, the radius of curvature of curved surface and its focal length in air are respectively
An objective is kept at a distance of from a thin lens and the image formed is real. If the object is kept at a distance of from the same lens the image formed is virtual. If the size of the images formed are equal, then find the focal length of the lens?
A double convex lens has focal length of in air. The radius of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii of curvature, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is .
Which of the following expression is correct for :
Taking the rays as incident from a medium of refractive index to another of refractive index
The image obtained with a convex lens is erect and its length is four times the length of the object. If the focal length of the lens is , the object and image distances are
A double convex lens, made of glass of refractive index , has its both surfaces of equal radii of curvature of each. An object of height is placed at a distance of from the lens. Find the size of the image.
A hollow double concave lens is made of very thin transparent material. It can be filled with air or either of two liquids or having refractive indices and respectively The lens will diverge a parallel beam of light if it is filled with
A concave lens of glass, having refractive index has both surfaces of same radius of curvature . On immersion in a medium of refractive index it will behave as a
What is focal length?
The radius of curvature of each surface of a convex lens having refractive index is . The lens is now immersed in a liquid of refractive index . The ratio of power of lens in air to its power in the liquid will be . The value of is
A bi convex lens of focal length is cut in two identical parts along a plane perpendicular to the principal axis. The power of each lens after cut is _____ .
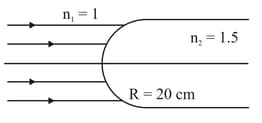
A parallel beam of light enters a medium through convex interface as shown. Find the distance at which the rays converge
The power of a lens (biconvex) is in particular medium. Refractive index of the lens is and radii of curvature are and respectively. The refractive index of surrounding medium:
A thin equiconvex lens is made of glass of refractive index and its focal length in air is m. If it acts as a concave lens of focal length when dipped in a liquid, the velocity of light in the liquid is
A convex lens of refractive index is immersed in a liquid of refractive index The lens will behave as a
The optical power of a lens is in air. Its optical power in a liquid of R.I. is
Focal length of a convex lens will be maximum for
